ABARES, Media Release, 24 February 2021
A new ABARES report today confirms agriculture has been one of the Australian economy’s standout performers in recent decades.
Snapshot of Australian Agriculture 2021 has found that the gross value of agricultural, fisheries and forestry production has risen over the past 20 years and, despite recent droughts, reached $67 billion in 2019–20.
While the value of agricultural exports has fluctuated between $40 billion and $60 billion during the same period, the value of meat and live animal exports has increased 86 per cent, with horticulture up 64 per cent.
ABARES’ acting executive director Jared Greenville said the sector’s rate of growth was testament to farmers’ ability to adapt, manage risk and seize opportunities.
“Agricultural productivity has outpaced most other sectors of the Australian economy over the long term,” Dr Greenville said.
“COVID 19 was a major event for the sector in 2019–20, but it demonstrated an ability to adapt and transition to new opportunities.
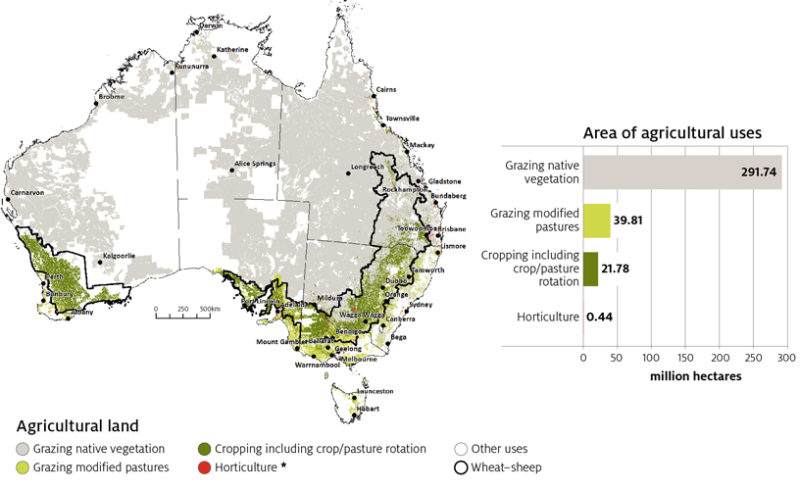
“Australian farmers successfully manage significant variability, including a highly variable climate and volatile commodity prices and have employed a number of effective strategies for managing those risks.
“Well-managed farms are better prepared for droughts and other risks, such as global price shocks, and not all farmers in regions affected by drought experience economic or financial hardship.”
The report takes a fresh overview of the industry, summarising key issues with descriptive statistics.
It also notes:
- Increased volume has been the main driver of growth in the cropping sector and higher prices driven growth in the livestock sector.
- Farm sizes have increased, in terms of both total receipts and land area, as the number of farms has decreased.
- Labour is a key input to Australian agriculture and total farm employment varies throughout the year in line with the timing of relatively labour-intensive operations.
- Government support of Australia’s agricultural sector is very low compared to the 37 member OECD countries.
- Australia’s trade agreements with major trading partners have provided access to new and growing markets over the past 15 years.
The Snapshot of Australian Agriculture 2021 is available here.